Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers in humans and is becoming more common. It occurs most often in Caucasian patients who tend to sunburn easily. Exposure to the sun is most often associated with skin cancer. It is also the cause that is the easiest to control. Each time skin is exposed to the sun, damage is caused. This damage accumulates over time. Childhood sunburns may show up as skin cancer twenty years later.
There are 3 common types of skin cancer:
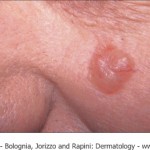
Basal Cell Carcinoma
This is the most common type of skin cancer. It usually appears as a small, transparent or pearly bump. As time passes, it will slowly grow and may crust and bleed. It can have other appearances. On the trunk of the body it can be a red, scaly, persistent patch. Some tumors can have pigment (turn brown or black) and some can resemble cysts. Rarely, they can look like a slowly enlarging scar. These tumors almost never spread to other areas of the body (metastasize). They can, however, grow locally and cause considerable problems.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
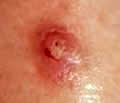
This is the second most common type of skin cancer. Chronic sun exposure is the most common cause, but X-ray, arsenic exposure, and many other factors can cause squamous cell carcinoma. The tumors appear as persistent, crusted and scaly bumps. They usually grow faster than basal cell carcinomas. They can also scab or become an open sore. Squamous cell carcinomas that occur on sun-damaged skin seem to be less serious than those that arise from other causes and rarely spread to other areas of the body. Most studies indicate that only 1 in 200 cases will spread. However, areas of the lip, in the mouth, or on the genital area are more serious and have a higher rate of spreading.
Malignant Melanoma
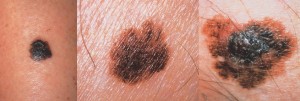
This is the least common of the three most common skin cancers. It is the most serious. It is a fairly rare tumor but is becoming more common. If you are white-skinned, the present lifetime risk is 1 in 130. The rate of melanoma has been doubling every ten years. Currently, there are about 6,000 deaths from melanoma every year in the USA. For comparison, the lifetime risk for a woman having breast cancer is 1 in 10.
Many people falsely believe that a diagnosis of melanoma is a death sentence. This is absolutely not true. This is a very curable disease when diagnosed and treated early. Most melanomas will grow on the top of the skin for months or years before they begin to grow down. If they are diagnosed and treated while still thin, less than 1 mm thick, the cure rate exceeds 95%.
50% of melanomas appear as new moles and 50% occur in existing moles. When watching for mole changes, remember the ABCD’s of melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half unlike the other half
- Border: Irregular, scalloped, or notched borders
- Color: Variable colors (tan, brown, black, red, etc.)
- Diameter: Greater than 6mm; the diameter of a pencil eraser
If you are at all concerned about any new spots on your skin, or if any of the above symptoms exist, please schedule an appointment with a dermatologist today.
External Links:
Basal cell carcinoma info at emedicine.com
Squamous cell carcinoma info at emedicine.com
Malignant melanoma info at emedicine.com
For more detailed information, please refer to the American Academy of Dermatology.